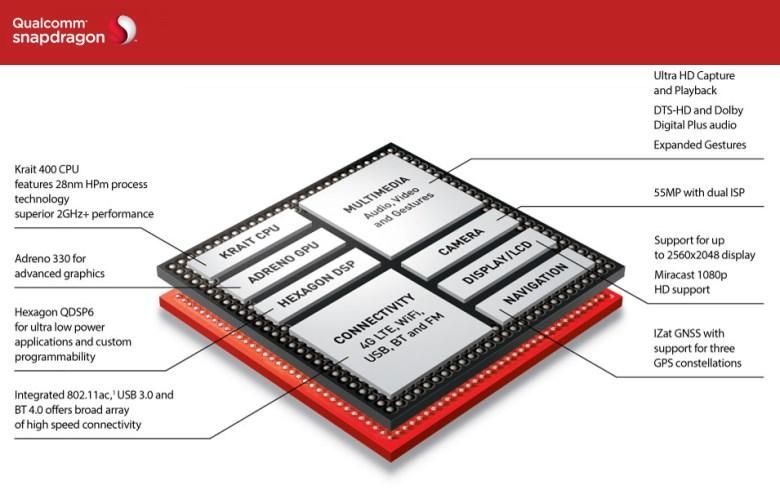
Inside every smartphone is a processor, but unlike your desktop or laptop computer, it’s not a single, discreet chip. Instead, smartphones employ something called a “system on a chip”, or SoC for short. Over the years these chips have gotten smaller, faster, and have incorporated more features and functionality. This time around it’s the Snapdragon 800 from Qualcomm that’s caught our eye.
Snapdragon 800 Processors are designed to deliver amazingly fast apps, stunning graphics, all without sacrificing battery life. If that sounds like every other SoC before it, you’re right. In every generation of processor, various manufacturers try to make their solution go faster, put off less heat, make things look better, and find innovative ways to do all those without sucking your battery dry in minutes.
At first glance you might be tempted to ignore Qualcomm’s marketing and hype as “just the next iteration” of their chip. You’re not wrong. It is hype, and it is the next iteration of their chip. The hype, however, is warranted, and the “iteration” of the Snapdragon 800 is worth your while.
Let’s dig in and see what sets this chip apart from the crowd, and why you’ll want the Snapdragon 800 in your next phone.
Processing Power
As technology marches ever onward, chips keep getting smaller. One of the ways they do so by employing construction methods and techniques that shrink the circuit paths inside the chip. The Snapdragon 800 features 28nm construction — that’s about 600 times smaller than a human hair. The small this number goes, the less expensive each unit usually ends up being, since less raw materials are needed in its construction. Also, smaller circuits require less power to run them, and they put off less heat. All of which are very attractive benefits when talking about processors, let alone mobile processors.
The Snapdragon 800 features a quad core Krait 400 central processing unit that can be clocked up to 2.3GHz per core. OEMs may choose to run the chip slower to improve battery life, but we all know that rooting and applying a custom kernel will get around that limitation.
Processing power isn’t of much help if the RAM that feeds bits to the CPU can’t keep up. The Snapdragon 800 supports LP-DDR3 memory, which is very high performance memory with and very low latency.
When most people think about multi-core processors they may think that all the processors run at the same speed. That’s not the case. Processors with multiple cores usually feature the ability to ramp speeds up and down, and may even run cores are different speeds, or not at all, depending on the load. The Snapdragon employs a feature called Asymmetrical Multi-Processing (aSMP) which produces some amazing results. Each core can throttle up and down depending on the tasks that you’re throwing at it. The result should be increased battery life without sacrificing performance.
Power Management
All that raw processing power is great, but we’re not talking about a desktop computer that’s tethered to a nuclear power plant, we’re talking about a phone with a very finite battery tucked neatly behind its screen. Luckily, Qualcomm has built the 800 with power management in mind. It features something called “Energy efficient High Performance for Mobile (HPm) technology” and aSMP dynamic CPU power control (which we talked about earlier). And, as we mentioned before, it’s got better thermal energy performance, which means it runs cooler and has better battery life.
But it’s still powered by the battery in your phone. Those batteries have another problem: they take a long time to charge. The Snapdragon 800 features an new “Quick Charge 2.0” specification which should speed up battery charging by up to 75%.
Since the 800 has a very low standby power requirement it’s got an ultra-low power voice activation feature which may or may not make it into a production device — that will be determined by each OEM as they build their devices. If OEMs do include it, you’ll be able to wake up your device by speaking a keyword. The chip does this by leveraging the device’s audio codec, digital signal processor, and CPU to deliver an end-to-end voice activation solution without having to touch the device or manually wake it up.
Graphics
A lot of what you perceive as CPU speed is actually GPU speed. You and I can’t really see the CPU in action. “Seeing” is something that’s realized by your display and the part of the SoC that powers it: the graphics processing unit.
Inside the Snapdragon 800 lies an updated Adreno 330 GPU which delivers up to 50% increase in graphics performance over what we’ve seen before. That doesn’t mean much to most people. Put into practice, it means the new chipset supports advanced graphics and various APIs, including OpenGL ES 3.0, DirectX, OpenCL, Renderscript Compute, and FlexRender™. What does all that mean to you? Graphics will look better. Video will be smoother. Games will look more realistic. And all of it will come without a noticeable impact on battery life.
Put yet another way, the Snapdragon’s GPU will support not only 1080P resolutions (which it can output to your big-screen TV wirelessly via Miracast), but it also supports the new 4K resolution. Yeah, it just got real!
Digital Signal Processor
Enough about graphics. The Snapdragon 800 includes some pretty hefty audio processing, too. At first you might think this is an unnecessary luxury, but since this chip runs your phone, and you do talk on it, you probably will be having some signal processing going on. That’s not all that a DSP does, of course. There’s a lot log legwork going on to process all kinds of signals digitally. To handle the workload of ever-increasing “signals” to process, the Snapdragon 800 includes the Hexagon QDSP6V5A, running at 600MHz. The Hexagon DSP enables ultra-low power operation for a variety of applications like music playback, enhanced audio, and even advanced editing applications.
Wired and Wireless Connectivity
Since a phone or tablet isn’t of much use without some sort of connectivity, you’ll be pleased to learn that the Snapdragon 800 includes “True 4G LTE World Mode” with LTE FDD, LTE TDD, WCDMA, CDMA1x, EV-DO, TD-SCDMA, and GSM 4G LTE with Carrier Aggregation.
Yeah, I know, that’s a whole lot of acronyms. What it means to you is that support for whatever high-speed cellular data your carrier provides is most likely included out-of-the-box, and enables speeds up to 150 Mbps right to your hand. Not every technology will be built-in to a single chipset. There will be several variants to enable each carrier’s flavor of data and network type.
Cellular data, however, isn’t everything, WiFi still plays a big role. As such, the 800 includes support for WiFi 802.11ac on both 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands, for the best WiFi experience you’re likely to get on a mobile device.
Bluetooth BT4.0 has been included for Low Energy devices and is ready for devices “of the future”.
How about wired connectivity? Sure thing! In addition to the standard USB 2.01, the Snapdragon 800 also includes USB 3.0 support for ultra-fast transfers. Again, whether or not this will make it to your device will be up to the manufacturer, and USB 3.0 does require a somewhat different cable to get the full speed benefits, so although the chip may support it, my gut tells me that most OEMs probably won’t.
GPS
Last, but certainly not least, let’s look at GPS and location services. The Snapdragon 800 includes support for GPS IZat GNSS which combines multiple location services into a single, high-performance geo-location system to help you know exactly where you are, and how to best get from there to wherever it is that you’re going.
All in all, the Snapdragon 800 is a very impressive chip, and one that I hope will be in my next smartphone. Would you like it in yours?